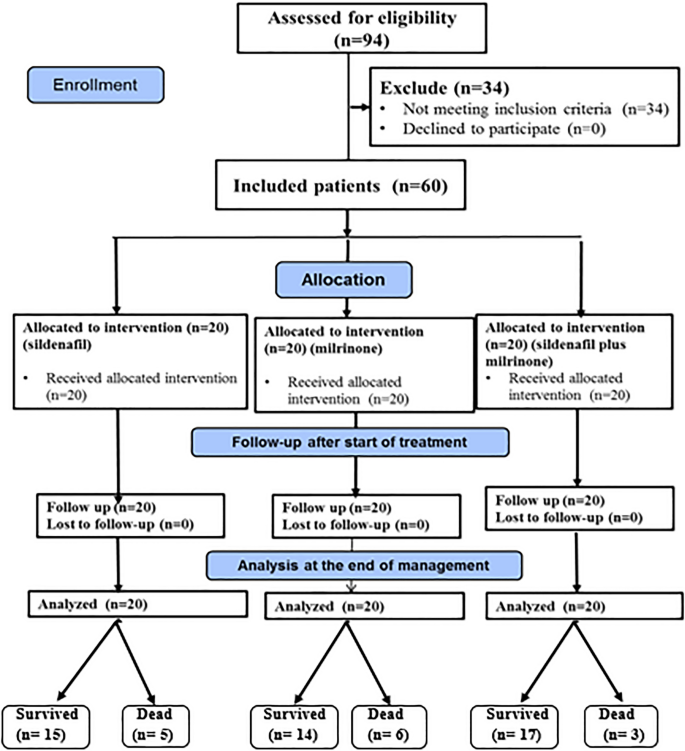
No, Viagra is not a standard treatment for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN). While some research explores its potential in specific, highly controlled contexts, it’s crucial to understand this isn’t a typical or recommended approach.
Current PPHN management primarily relies on inhaled nitric oxide, ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation), and medications like sildenafil (Revatio) – a closely related drug. Sildenafil, unlike Viagra, has a specific FDA approval for PPHN treatment. The differences in formulation and dosage are significant, demanding strict adherence to medical guidance.
Always consult your physician or neonatologist for PPHN treatment. They will determine the appropriate therapy based on the severity of your child’s condition and their individual needs. Self-treating PPHN with Viagra or any other medication without professional supervision is extremely dangerous and could have severe consequences.
Remember: This information provides a general overview and should not replace professional medical advice. Seek immediate medical attention for any suspected case of PPHN.
- Viagra for PPHN: A Detailed Overview
- Dosage and Administration
- Potential Side Effects
- Monitoring and Management
- Comparison with Other Treatments
- Conclusion
- Understanding Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Newborn (PPHN)
- Causes of PPHN
- Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Treatment Approaches
- Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook
- Viagra’s Mechanism of Action in Treating PPHN
- Impact on Pulmonary Artery Pressure
- Considerations for Treatment
- Clinical Applications and Efficacy of Viagra for PPHN
- Dosage and Administration
- Clinical Evidence and Outcomes
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- Conclusion
- Current Research and Future Directions in Viagra’s Use for PPHN
Viagra for PPHN: A Detailed Overview
Sildenafil (Viagra) offers a viable treatment option for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN). It acts by relaxing pulmonary blood vessels, improving blood flow to the lungs. This reduced pulmonary vascular resistance helps improve oxygenation in affected newborns.
Dosage and Administration
Sildenafil dosage varies depending on the infant’s weight and response to treatment. A physician carefully monitors the infant’s condition, adjusting the dose as needed. Administration typically involves intravenous or oral routes, chosen based on the individual case. Close monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation is vital.
Potential Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, side effects can occur. These may include hypotension (low blood pressure), changes in heart rate, and gastrointestinal issues. Rarely, more serious side effects might manifest. Prompt medical attention is necessary should any adverse reactions appear. Careful monitoring mitigates risks.
Monitoring and Management
Regular monitoring of vital signs is crucial. This includes continuous assessment of oxygen saturation, blood pressure, and heart rate. Echocardiography may be used to assess heart function. Blood tests are performed regularly to monitor liver and kidney function, ensuring safe and appropriate administration.
Comparison with Other Treatments
| Treatment | Mechanism of Action | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhaled nitric oxide | Direct pulmonary vasodilation | Rapid onset of action | Requires specialized equipment, potential for systemic effects |
| Sildenafil | Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-5 | Oral and IV administration, fewer side effects | Slower onset than inhaled nitric oxide |
| Prostaglandins | Maintain ductus arteriosus patency | Improve systemic blood flow | Potential for side effects, less targeted impact on pulmonary vessels |
Conclusion
Sildenafil represents a valuable addition to the therapeutic arsenal for PPHN management. Individualized treatment plans, guided by careful monitoring and a physician’s expertise, maximize benefits and minimize potential risks.
Understanding Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Newborn (PPHN)
PPHN is a serious condition where a newborn’s blood vessels in the lungs remain constricted after birth. This prevents enough oxygen from entering the bloodstream, leading to low blood oxygen levels (hypoxemia). The condition affects approximately 1 in 1,000 newborns.
Causes of PPHN
Several factors contribute to PPHN. These include meconium aspiration (inhalation of meconium during delivery), group B streptococcal infection, congenital diaphragmatic hernia (a birth defect affecting the diaphragm), and various lung conditions. Sometimes, the cause remains unknown.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms vary, but often include rapid breathing, bluish skin discoloration (cyanosis), and low oxygen saturation levels measured with a pulse oximeter. Diagnosis involves a physical exam, chest X-ray, and echocardiogram to assess heart function and blood flow through the lungs. Blood gas analysis directly measures oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood, confirming the severity of the condition.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment focuses on improving oxygen levels and reducing pulmonary vascular resistance. This often involves supplemental oxygen, inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) to relax blood vessels, and mechanical ventilation to support breathing. In severe cases, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) may be necessary to provide temporary heart and lung support. Medication, such as Viagra (sildenafil), might be administered to widen blood vessels in the lungs and improve blood flow.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook
The outcome for infants with PPHN depends on several factors, including the severity of the condition, the underlying cause, and the promptness and effectiveness of treatment. Early intervention is vital. Some infants fully recover, while others may experience long-term lung problems or other health issues requiring ongoing care. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring recovery and addressing any potential complications.
Viagra’s Mechanism of Action in Treating PPHN
Sildenafil, the active ingredient in Viagra, treats persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) by targeting the pulmonary vasculature. It selectively inhibits phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5), an enzyme that breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). Increased cGMP levels relax smooth muscle in the pulmonary arteries, lowering pulmonary vascular resistance. This improved blood flow allows more oxygen-rich blood to reach the lungs and body.
Impact on Pulmonary Artery Pressure
The reduced pulmonary artery pressure facilitates better gas exchange. This crucial action improves oxygen saturation in the blood, significantly benefiting infants with PPHN. The medication’s effect is a direct consequence of its ability to increase cGMP and subsequently relax the constricted pulmonary vessels. Clinical trials demonstrate this effect; however, individual responses vary.
Considerations for Treatment
While sildenafil offers a valuable treatment option, it’s critical to remember that PPHN management often involves a multifaceted approach. Monitoring oxygen saturation and blood pressure is essential, alongside careful consideration of potential side effects. Always consult a neonatologist for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies.
Clinical Applications and Efficacy of Viagra for PPHN
Sildenafil, the active ingredient in Viagra, demonstrates efficacy in treating persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) by improving pulmonary vascular tone. It achieves this by inhibiting phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5), leading to increased levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) and subsequent pulmonary vasodilation.
Dosage and Administration
Typical sildenafil administration for PPHN involves intravenous infusion. Dosage varies depending on the infant’s weight and response, with close monitoring of blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and other vital signs imperative. A physician carefully determines the optimal dosage and duration of therapy.
- Initial doses generally range from 0.1 to 0.2 mg/kg.
- Titration is common to achieve the desired hemodynamic effect.
- Careful monitoring prevents adverse effects.
Clinical Evidence and Outcomes
Numerous studies support sildenafil’s use in PPHN. Improved oxygenation and reduced need for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) are frequently reported. However, individual responses vary.
- Studies show significant improvements in pulmonary artery pressure.
- Oxygen saturation levels often increase.
- Reduced need for mechanical ventilation is observed in many cases.
- Improved survival rates have been noted in certain studies.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While generally well-tolerated, potential side effects include hypotension, flushing, and visual disturbances. Careful monitoring and prompt adjustments to the dosage are necessary. Pre-existing conditions, such as retinopathy, require cautious consideration before initiating sildenafil therapy.
Conclusion
Sildenafil offers a valuable therapeutic option for managing PPHN, offering potential improvements in hemodynamics and clinical outcomes. However, individualized treatment plans and meticulous monitoring are crucial for optimal results and minimizing potential adverse effects. Always consult with a medical professional for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Current Research and Future Directions in Viagra’s Use for PPHN
Researchers are actively exploring Viagra’s potential in improving targeted therapies for PPHN. Clinical trials are investigating optimized dosing regimens and exploring combination therapies with other pulmonary vasodilators to enhance efficacy and minimize side effects. This includes studies evaluating different routes of administration, aiming for improved delivery and bioavailability of sildenafil.
Improved diagnostic tools are crucial. Studies are focusing on identifying biomarkers to predict which infants will respond best to Viagra treatment. This personalized approach promises to significantly improve treatment outcomes. Early detection of non-responders allows for timely alternative treatments.
Long-term follow-up studies are needed to assess the long-term pulmonary and cardiovascular effects of Viagra treatment in infants with PPHN. These studies will provide valuable data on potential late-onset complications and inform future clinical practice guidelines. Research into the specific mechanisms of action of sildenafil in PPHN is also ongoing, potentially uncovering new therapeutic targets.
Genetic research plays a vital role. Scientists are investigating genetic factors influencing the response to Viagra therapy. This research will help to identify patients most likely to benefit and those at higher risk of adverse effects, guiding clinical decision-making. The ultimate goal is to develop predictive models for treatment response based on genetic profiles.
Future research directions also involve exploring novel drug delivery systems such as targeted nanoparticles for improved drug delivery to the pulmonary vasculature. This approach would improve drug efficacy and reduce systemic side effects. Simultaneously, research into alternative phosphodiesterase inhibitors is underway, aiming to discover molecules with improved safety and efficacy profiles.